Abstract
Background: The growth factor receptor bound protein-2 (Grb2) is vital to tumor progression. Prexigebersen (BP1001) is a liposome-incorporated Grb2 antisense oligonucleotide that inhibits Grb2 expression. Grb2 inhibition suppresses cancer growth and survival. A Phase I/IB single center study (Ohanian, Lancet Haematol 2018) in relapsed/refractory AML patients (pts) demonstrated BP1001 safety up to 90 mg/m2 and demonstrated CR/CRi in 3/6 relapsed/refractory AML pts treated with BP1001 + low dose cytarabine (LDAC) in the Phase IB portion. Based on PK considerations, the recommended Phase II dose was 60 mg/m2. A phase II study was initiated to explore the clinical impact of BP1001 in untreated AML pts considered unsuitable for standard chemotherapy.
Methods: This is a multi-center open-label, Phase II study in untreated AML pts to determine the safety and preliminary efficacy of BP1001 (given at 60 mg/m2 over 1-3 h twice weekly for a total of 8 doses over a 28-day cycle) in combination with LDAC (starting after the Day 4 dose, 20 mg twice daily for 10 days). Eligible pts were considered unsuitable for or refused intensive chemotherapy and had ECOG performance status of 0-2. Blood samples were taken on Days 1 and 11 to determine BP1001 plasma pharmacokinetics (PK).
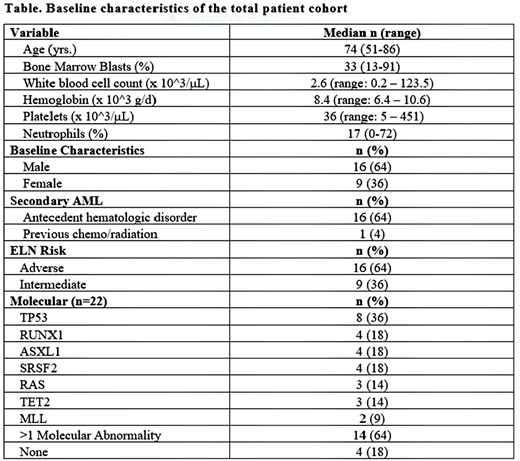
Results: A total of 25 pts (16 male: 64%) with a median age of 74 years (range, 51-86 years) was treated with at least 1 cycle of BP1001 + LDAC. Sixty-eight percent (17/25) had secondary AML evolved from MDS (n=13) or MPN (n=3) or prior chemotherapy/radiotherapy (n=1). The majority (64%) had adverse-risk (ELN classification); 36% were intermediate-risk. Infusional reactions (IR) (rigors, fevers, or chills) were observed in 20% of pts when the infusion rate was 1 h. IR were mild, controlled with supportive measures, and were not observed when the infusion rate was 2 h. Other AE's were generally consistent with those expected with LDAC and/or AML, including fatigue (64%), diarrhea (24%), neutropenic fever (24%), and pneumonia (20%). The most frequent SAEs were pneumonia (20%) and neutropenic fever (24%).
Four pts died within 30 days of treatment (between days 20-27), all of AML-related complications (including intracranial hemorrhage, pneumonia, septic shock, and splenic rupture). Ten pts had documented progressive disease. Two pts withdrew consent after 1 cycle of treatment. Evaluability of efficacy was defined as: receipt of at least 4 cycles of therapy, PD, or CR/CRi prior to 4 cycles. PK data revealed that the Time of maximal observed concentration (Tmax), the mean terminal elimination half-life (t1/2), and the area under the curve from zero to the last quantifiable concentration (AUC(last)) for BP1001 were similar between Days 1 and 11. Tmax of BP1001 was 1.9 vs 2.3 h (day 1 vs 11); t1/2 was 5.2 vs 5.7 h; AUC(last) was 308 vs 275 h*ng/mL.
Response: Among 17 fully evaluable pts, 7 pts (41%) demonstrated bone marrow blast reduction, including 5 (29%) who achieved a CR (n=3), CRi (n=1), or morphologic leukemia free state (n=1). Two additional pts demonstrated a ≥50% reduction of bone marrow blasts (from 20% to 9% and from 71% to 8%), including 1 with hematologic improvement of the absolute neutrophil count. The median overall survival (OS) was 5.2 months (range, 0.6-15.2) for all patients. For evaluable patients, the median OS was 6.3 months (0.8-15.2 months). The CRs included: a 74-year old female who achieved CR after 2 cycles of therapy and then received 2 additional cycles followed by a matched-sibling allogeneic transplant. She remained in CR for 10 months before first relapse. A 73-year old female, with AML transformed from MDS, benefited from therapy despite refusal of blood products due to religious objections. Her hemoglobin declined to 4.0 g/dL during therapy but recovered to as high as 9.9 g/dL once in CR after 4 cycles. An 86-year old male achieved CR after 4 cycles of therapy and maintained CR for 3 months before relapse.
Conclusions: BP1001 has been safely administered to 25 pts with untreated AML, who were considered unsuitable for standard chemotherapy. Efficacy data are encouraging in a challenging population in which the majority of pts had secondary AML or adverse-risk AML, and compares favorably to the reported CR/CRi/CRp rate with LDAC of 7-13% (Heiblig, Mediterr J Hematol 2016; Kantarjian, J Clin Oncol 2012; Döhner, Blood 2014). A protocol amendment made to optimize BP1001 administration with LDAC and to add a decitabine combination arm is in place.
Lin:Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria. Ritchie:Incyte: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Astellas Pharma: Research Funding; NS Pharma: Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; ARIAD Pharmaceuticals: Speakers Bureau; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses, Speakers Bureau. Craig:Celgene: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Actinium Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding. Agrawal:Incyte: Speakers Bureau. Pemmaraju:Affymetrix: Research Funding; plexxikon: Research Funding; daiichi sankyo: Research Funding; SagerStrong Foundation: Research Funding; samus: Research Funding; celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; abbvie: Research Funding; cellectis: Research Funding; stemline: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; novartis: Research Funding. Tari Ashizawa:Bio-Path Holdings, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership, Patents & Royalties. Hahne:Bio-Path Holdings, Inc.: Employment. Cortes:Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy, Research Funding; Astellas Pharma: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Arog: Research Funding. Roboz:Orsenix: Consultancy; Astex Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Argenx: Consultancy; Cellectis: Research Funding; Roche/Genentech: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Janssen Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Aphivena Therapeutics: Consultancy; Celltrion: Consultancy; Otsuka: Consultancy; Sandoz: Consultancy; Orsenix: Consultancy; Roche/Genentech: Consultancy; Celgene Corporation: Consultancy; Astex Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; AbbVie: Consultancy; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy; Cellectis: Research Funding; Aphivena Therapeutics: Consultancy; Janssen Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Otsuka: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Eisai: Consultancy; Eisai: Consultancy; Argenx: Consultancy; Sandoz: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Celgene Corporation: Consultancy; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy; AbbVie: Consultancy; Bayer: Consultancy; Celltrion: Consultancy; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Bayer: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal